Introduction
Food businesses across the world operate in an increasingly demanding environment. Consumers expect safety and hygiene as a basic requirement. Regulators impose strict compliance frameworks. Global buyers expect scientific systems that prevent contamination, control hazards, ensure traceability and maintain consistent product quality.
This is where HACCP Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points plays a central role. HACCP is a preventive, science based approach designed to identify, evaluate and control hazards throughout every stage of food production. It is the foundation of modern food safety systems and is integrated into global standards including FSSAI, ISO 22000, FSSC 22000, BRCGS and Codex Alimentarius.
Emaza Services Pvt. Ltd. supports organisations across food manufacturing, FMCG, beverages, bakery, dairy, packaging, retail and food services with complete HACCP implementation including gap assessments, documentation, process mapping, hazard analysis, training, internal audits and certification readiness. With strong experience in sustainability frameworks such as SEDEX SMETA, QIMA and EcoVadis, Emaza ensures that food safety systems are aligned not only with compliance but also with responsible, ethical and environmentally conscious operations.
This guide provides a comprehensive HACCP implementation roadmap for food businesses that want to strengthen safety, ensure compliance and achieve global market acceptance.
Understanding HACCP and Its Importance
HACCP is a systematic, preventive approach that focuses on identifying and controlling potential hazards that could affect food safety. Instead of relying on final product testing, HACCP ensures that hazards are controlled at the source through scientific monitoring and verification.
Why HACCP is essential for modern food businesses
• Mandatory requirement under FSSAI for many categories
• Core requirement of global certifications
• Reduces risk of contamination
• Enhances food safety and consumer confidence
• Strengthens export eligibility
• Improves traceability and accountability
• Prevents costly product recalls
• Integrates with sustainability goals through waste reduction and efficient operations
HACCP also helps organisations meet buyer expectations related to safety, hygiene and responsible manufacturing.
Prerequisite Programs Required Before HACCP Implementation
Before implementing HACCP, the organisation must establish strong prerequisite programs PRPs. These are the foundation of food safety.
Key PRPs
• Good Manufacturing Practices
• Good Hygiene Practices
• Cleaning and sanitation programs
• Pest control
• Calibration of equipment
• Supplier approval
• Allergen control
• Waste management
• Personal hygiene standards
• Water and air quality control
Emaza supports organisations in strengthening each PRP before beginning HACCP development.
The Seven Principles of HACCP
A Scientific and Structured Approach
HACCP implementation is built on seven globally accepted principles.
Principle 1: Conduct Hazard Analysis
Identify biological, chemical and physical hazards at each stage of the process.
Principle 2: Determine Critical Control Points
Identify specific points where hazards must be controlled to ensure safety.
Principle 3: Establish Critical Limits
Define measurable values such as temperature, time and pH that ensure hazard control.
Principle 4: Establish Monitoring Procedures
Define who monitors, how often they monitor and what method is used.
Principle 5: Establish Corrective Actions
Define actions to be taken when a critical limit is not met.
Principle 6: Establish Verification Procedures
Ensure that monitoring is effective and the system is working as intended.
Principle 7: Establish Documentation and Record Keeping
Create all required documents, forms and logs to demonstrate safety control.
These principles guide every HACCP implementation project and ensure global acceptance.
HACCP Implementation Roadmap
A Complete Step by Step Framework
Emaza Services follows a practical, industry validated roadmap for HACCP implementation.
Step 1: Initial Assessment
Evaluate facility layout, hygiene, documentation, processes, equipment and compliance status.
Step 2: Define Scope and Product Description
Clearly define the products covered under HACCP and their characteristics such as composition, allergens and packaging.
Step 3: Identify Intended Use
Define how the consumer is expected to use the product.
Step 4: Create Process Flow Diagram
A complete flow covering raw materials, processing, packaging, storage and distribution.
Step 5: On Site Verification of Process Flow
Ensure that the flow chart reflects the actual operational process.
Step 6: Hazard Analysis
Evaluate potential biological, chemical and physical hazards at each processing step.
Step 7: Determine CCPs
Use the CCP decision tree to define critical control points.
Step 8: Establish Critical Limits
Define measurable parameters for each CCP.
Step 9: Develop Monitoring Procedures
Develop monitoring frequency, method and responsibility.
Step 10: Define Corrective Actions
Create corrective action steps in case of deviation.
Step 11: Establish Verification Procedures
Include validation, internal audits, calibration and periodic reviews.
Step 12: Record Keeping and Documentation
Prepare
• HACCP plan
• CCP monitoring forms
• Verification records
• Corrective action records
• Hazard analysis documents
This structured roadmap ensures complete compliance and audit readiness.
Hazard Categories in HACCP
1. Biological
• Bacteria
• Viruses
• Parasites
• Yeasts and molds
2. Chemical
• Allergens
• Cleaning agents
• Pesticide residues
• Food additives
3. Physical
• Metal fragments
• Glass
• Plastic pieces
• Stone or wood particles
Hazards vary depending on product category and processing methods.
HACCP Decision Tree
Determining CCPs Scientifically
A decision tree helps teams determine whether a step is a CCP. Typical questions include
• Does a hazard exist at this step
• Is control at this step necessary for safety
• Can a hazard be prevented or reduced here
• Will subsequent steps eliminate or reduce the hazard
This ensures consistency and accuracy in identifying CCPs.
Common CCPs in Food Processing
• Cooking
• Cooling
• Freezing
• Metal detection
• Sieving
• Fermentation
• pH control
• Allergens segregation
• Water filtration
Each CCP requires monitoring, verification and documented evidence.
HACCP Documentation System
Organised, Simple and Audit Ready
An effective documentation system includes
• HACCP manual
• Process flow chart
• Hazard analysis reports
• CCP determination
• Critical limits
• Monitoring logs
• Corrective action forms
• Verification and validation reports
• Supplier records
• Traceability documentation
Emaza designs user friendly documents aligned with daily operations.
HACCP and Sustainability Integration
HACCP contributes to sustainability and responsible operations through
• Reduction of wastage through process control
• Efficient resource management
• Safer production practices
• Improved traceability and responsible sourcing
• Lower batch rejections leading to reduced waste
Alignment with SEDEX SMETA, QIMA and EcoVadis ensures that food safety also supports ethical and environmental responsibility.
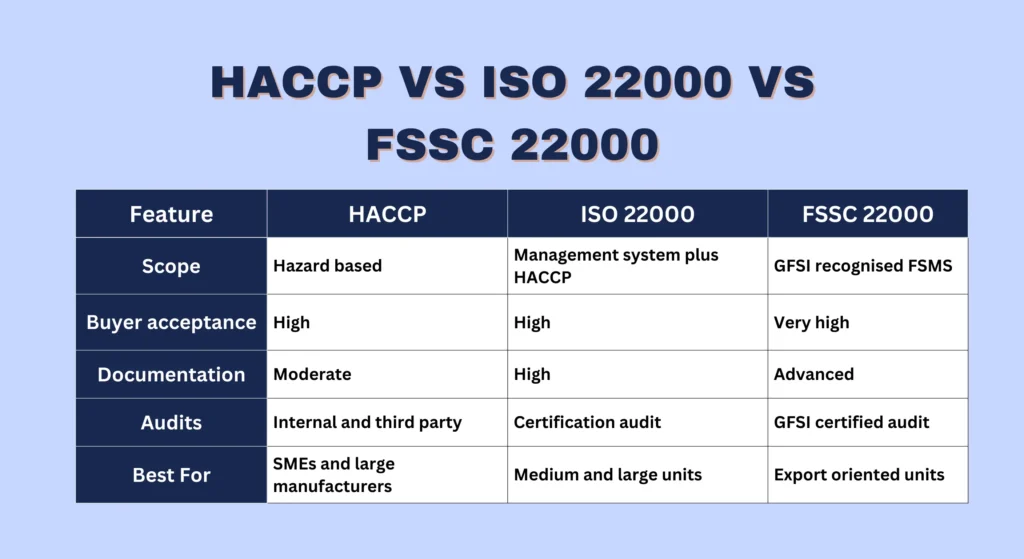
Table: HACCP vs ISO 22000 vs FSSC 22000
| Feature | HACCP | ISO 22000 | FSSC 22000 |
| Scope | Hazard based | Management system plus HACCP | GFSI recognised FSMS |
| Buyer acceptance | High | High | Very high |
| Documentation | Moderate | High | Advanced |
| Audits | Internal and third party | Certification audit | GFSI certified audit |
| Best For | SMEs and large manufacturers | Medium and large units | Export oriented units |
All three systems strengthen food safety but differ in their structure.
Common Challenges in HACCP Implementation
• Incorrect process flow diagram
• Weak prerequisite programs
• Incomplete hazard analysis
• Misidentified CCPs
• Inconsistent monitoring
• Inadequate training
• Lack of verification procedure
• Poor documentation
• Limited team ownership
Emaza helps organisations resolve these challenges with structured guidance and targeted training.
Case Study
A Dairy Processing Unit Strengthens Safety Through HACCP Implementation
A dairy manufacturing company faced inconsistent product quality, microbial complaints and regulatory non conformities.
Challenges
• No hazard analysis
• Weak hygiene practices
• Limited monitoring systems
• Inconsistent temperature control
Emaza’s Approach
• Full HACCP gap assessment
• Strengthened GMP and hygiene practices
• Detailed hazard analysis
• Identification of CCPs
• Monitoring plan creation
• Worker training on HACCP
• Internal audits
Results
• Improved product safety
• Reduced microbial counts
• Stronger regulatory compliance
• Improved customer confidence
• Better operational discipline
HACCP Monitoring and Verification
Ensuring System Effectiveness
Monitoring
Includes
• Temperature checks
• pH monitoring
• Visual checks
• Time recording
• Metal detector verification
Verification
Includes
• Calibration
• Testing
• Internal audits
• CCP validation
• Management review
Combination of both ensures effective control.
HACCP Audit Readiness
Preparing for Certification or Buyer Audits
Food businesses preparing for HACCP audits must ensure
• All CCP records are complete
• Monitoring logs are accurate
• Corrective actions are documented
• Verification records are available
• Worker training records are maintained
• Facility meets hygiene and sanitation requirements
Emaza performs mock audits to ensure readiness.
Future Trends in HACCP and Food Safety
• Digital HACCP systems
• AI based monitoring
• Real time temperature sensors
• Automated record keeping
• Stronger traceability systems
• Integrated food safety and sustainability reporting
• Stricter global buyer requirements
Businesses adopting these trends early will gain a competitive advantage.

Conclusion
HACCP is the foundation of modern food safety and is essential for regulatory compliance, operational efficiency and global buyer acceptance. Implementing HACCP strengthens process control, prevents contamination, reduces waste and ensures consistent product quality. When combined with sustainability frameworks such as SEDEX SMETA, QIMA and EcoVadis, HACCP contributes to safer and more responsible food production.
Emaza Services Pvt. Ltd. supports food businesses with complete HACCP implementation including hazard analysis, documentation development, CCP determination, monitoring systems, training programs and audit preparation. With experience across global compliance and sustainability systems, Emaza ensures that clients achieve strong, reliable and future ready food safety systems.