Introduction
Global consumers, retailers and governments are placing increasing emphasis on how products are made, who makes them and under what conditions. Ethical trade is no longer an optional addition but a fundamental requirement for any organisation that wants to participate in global markets. For exporters in food, FMCG, packaging, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and consumer goods, ethical compliance is now a direct business determinant because global buyers refuse to work with suppliers who cannot demonstrate fair practices, worker safety, responsible sourcing and transparent operations.
SEDEX SMETA has emerged as one of the most widely recognised frameworks for ethical trade and social compliance. It is accepted globally by multinational brands, importers, retailers and responsible sourcing programs. Implementing SEDEX SMETA helps organisations establish ethical business practices across labour, environment, safety, sustainability and governance, allowing them to confidently engage with international buyers.
Emaza Services Pvt. Ltd. supports organisations across multiple industries with complete SEDEX SMETA consulting, audit preparation, documentation development, worker welfare systems, responsible sourcing frameworks, environmental controls and long term sustainability integration. With extensive experience in global compliance systems such as QIMA and EcoVadis alongside SEDEX, Emaza provides a holistic approach that prepares export businesses for modern ethical and sustainability expectations.
This guide explores the complete requirements of SEDEX SMETA, its significance for export businesses and how organisations can implement it effectively for long term compliance and global acceptance.
Understanding SEDEX and SMETA
SEDEX Supplier Ethical Data Exchange is a global platform that allows companies to share ethical compliance information with buyers. It promotes transparency, responsible sourcing and socially acceptable business operations.
SMETA Sedex Members Ethical Trade Audit is the audit methodology used to evaluate a supplier’s ethical performance. It covers four core pillars.
The Four Pillars of SMETA
• Labour standards
• Health and safety
• Environment
• Business ethics
These pillars combine globally accepted frameworks including
• International Labour Organization standards
• Ethical Trading Initiative Base Code
• National labour laws
• Global responsible sourcing expectations
• Environmental and worker safety guidelines
SMETA audits are widely accepted by European, American and Asian importers, making them essential for export ready businesses.
Why SEDEX SMETA Is Critical for Export Businesses
Export businesses face heightened scrutiny because global retailers have strict responsible sourcing policies. SEDEX SMETA helps organisations demonstrate transparency and ethical performance.
Key benefits for suppliers
• Higher trust from international buyers
• Simplified supplier onboarding
• Opportunity to partner with multinational brands
• Improved worker welfare and safety
• Better environmental practices
• Reduced supply chain risks
• Fewer compliance related disruptions
• Stronger sustainability credentials
SEDEX participation creates long term growth opportunities for organisations with responsible and transparent practices.
SEDEX SMETA and Sustainability Integration
SEDEX SMETA aligns closely with global sustainability frameworks. Exporters often combine SEDEX with QIMA and EcoVadis because together they offer a complete picture of social, ethical, environmental and governance performance.
How SEDEX integrates with
EcoVadis
EcoVadis evaluates sustainability performance across environment, labour, ethics and sustainable procurement. SMETA data contributes to strong scoring in these categories.
QIMA
QIMA evaluates factories on ethical sourcing, worker welfare, environment and quality systems. A SMETA ready factory performs better on QIMA audits.
Together, these frameworks support a strong compliance ecosystem and significantly increase supplier acceptance.
Key Requirements of SEDEX SMETA
SMETA audits evaluate the organisation across detailed and structured criteria.
1. Labour Standards
• No forced labour
• No child labour
• Fair working hours
• Transparent wage structure
• Legal social security compliance
• Equal opportunity and non discrimination
• Worker welfare and grievance systems
2. Health and Safety
• Safe working conditions
• Fire safety
• Emergency preparedness
• PPE availability
• Chemical safety controls
• Machinery safety guards
• First aid and medical care
3. Environment
• Waste management
• Water and energy use monitoring
• Hazardous material handling
• Environmental impact control
• Compliance with local regulations
4. Business Ethics
• Anti corruption practices
• Transparent supplier engagement
• Legal compliance
• Fair business behaviour
• No unethical purchasing practices
SMETA goes beyond documentation and checks real operations, worker interviews and facility conditions.
SEDEX SMETA Implementation Roadmap
A Step by Step Framework for Businesses
Emaza Services follows a structured approach to ensure smooth and accurate implementation.
Step 1: Initial Assessment
Evaluation of current practices related to labour, health and safety, environment and ethics.
Step 2: Gap Analysis
A detailed SMETA gap assessment highlights
• Non conformities
• Legal gaps
• Documentation gaps
• Worker welfare issues
• Environmental risks
• Safety improvements required
Step 3: Documentation Preparation
Emaza prepares or upgrades required documentation including
• Policies for labour and human rights
• Wage and attendance registers
• Health and safety procedures
• Worker welfare programs
• Environmental monitoring records
• Ethics and anti corruption policies
• Supplier codes of conduct
Step 4: Facility and Welfare Improvements
SMETA audits check the real conditions in which workers operate. Improvements may include
• Fire safety upgrades
• Health and safety signage
• Drinking water and washroom facilities
• Ergonomic improvements
• Safe chemical storage
• Waste segregation
Step 5: Worker Training and Awareness
Training modules include
• Labour rights
• Safety procedures
• Emergency response
• Grievance mechanisms
• Environmental responsibilities
Step 6: Internal Audit
A SMETA style audit is conducted to identify final gaps.
Step 7: Corrective Action Planning
Any remaining issues are addressed based on internal audit findings.
Step 8: SMETA Audit Preparation
Emaza ensures complete readiness before the external audit.
SEDEX SMETA Compliance Checklist
Labour Standards
• Age verification
• Fair wages
• No excessive overtime
• Worker contracts
• Grievance mechanism
• No discrimination
Health and Safety
• Fire extinguishers with inspection tags
• First aid boxes
• PPE availability
• Safe chemical handling practices
• Emergency exits and evacuation plans
Environmental
• Waste logbook
• Effluent management
• Energy consumption records
• Environment policy
• Recycling initiatives
Business Ethics
• Anti bribery policy
• Legal compliance records
• Supplier code of conduct
• Ethical purchasing procedures
This checklist becomes the foundation for smooth SMETA preparation.
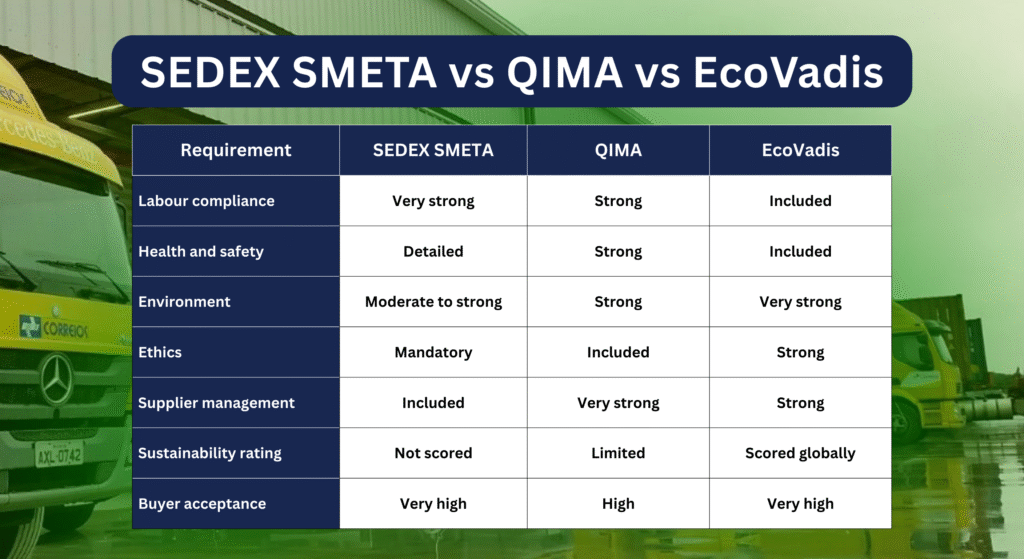
Table: SEDEX SMETA vs QIMA vs EcoVadis
| Requirement | SEDEX SMETA | QIMA | EcoVadis |
| Labour compliance | Very strong | Strong | Included |
| Health and safety | Detailed | Strong | Included |
| Environment | Moderate to strong | Strong | Very strong |
| Ethics | Mandatory | Included | Strong |
| Supplier management | Included | Very strong | Strong |
| Sustainability rating | Not scored | Limited | Scored globally |
| Buyer acceptance | Very high | High | Very high |
This combination creates a complete global compliance profile for suppliers.
Case Example
A Food Export Company Achieves SMETA Acceptance Through System Improvements
A mid sized food processing company wanted to expand exports to the European market. Buyers required SMETA audit reports and strong sustainability performance before approval.
Challenges
• Limited worker welfare documentation
• Gaps in safety training
• Inconsistent overtime records
• No environmental monitoring
• Weak grievance mechanism
Emaza’s Approach
• Complete SMETA gap assessment
• Documentation upgrade and standardisation
• PPE implementation and fire safety improvements
• Worker training on rights and safety
• Environmental monitoring setup
• Ethics and anti corruption policy deployment
• Internal audits and corrective actions
Results
• Successful SMETA audit
• Approved as a long term supplier
• Improved worker welfare and safety
• Stronger market acceptance
• Reduced compliance risks
Common Mistakes in SMETA Preparation
• Incorrect wage and overtime records
• Missing worker contracts
• Unsafe chemical storage
• Poor housekeeping
• Untrained safety personnel
• Incomplete environment documentation
• No ethics policy
• Worker interviews not prepared
Avoiding these issues ensures smoother audits.
Future Trends in Ethical Trade and Supply Chain Compliance
• Rising ESG expectations from buyers
• Demand for transparent labour practices
• Digital worker welfare records
• Traceability of ethical sourcing
• Combined audits for SEDEX, QIMA and EcoVadis
• Carbon reporting and environmental scoring
• Stronger focus on human rights due diligence
Businesses that integrate SEDEX SMETA early will stay ahead of global requirements.

Conclusion
SEDEX SMETA is one of the most influential ethical trade frameworks for export businesses. It ensures that companies operate responsibly, protect workers, follow safety and environmental norms and maintain transparent business practices. Exporters that adopt SMETA gain higher trust from international buyers, increased market opportunities and a stronger sustainability profile.
Emaza Services Pvt. Ltd. provides complete SEDEX SMETA consulting including gap assessments, documentation development, worker welfare programs, environmental monitoring assistance, internal audits and audit readiness support. With combined expertise in SEDEX, QIMA and EcoVadis, Emaza helps organisations build holistic, responsible and globally compliant operations.











